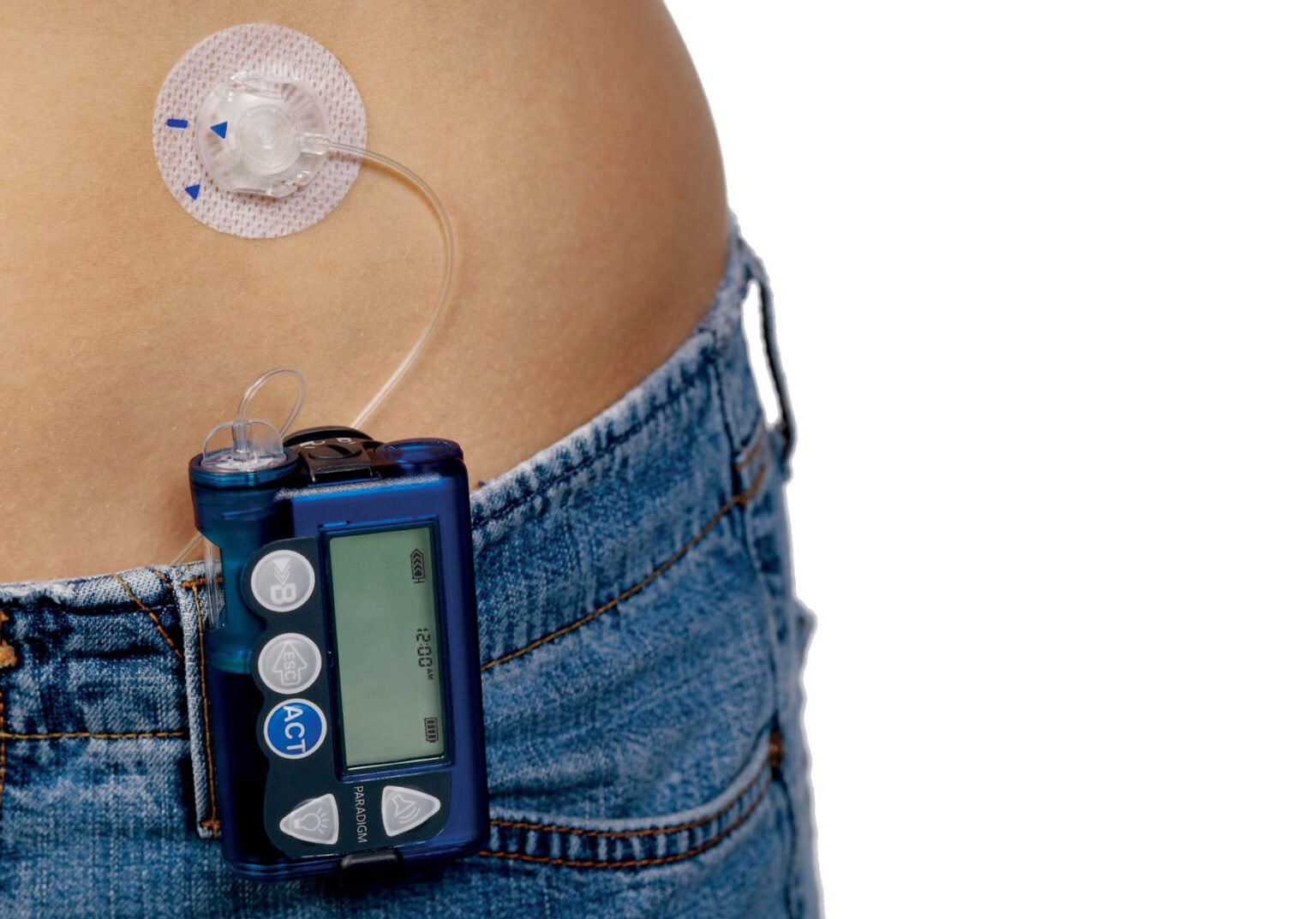
Insulin pumps have transformed diabetes management, offering a more precise and adaptable approach to insulin therapy compared to traditional injections. These small, portable devices deliver insulin continuously under the skin, supporting patients in maintaining optimal blood glucose levels and reducing long-term diabetes complications.
The device typically consists of three main components: the pump itself, which includes controls and a battery; a disposable insulin reservoir that fits inside the pump; and a disposable infusion set with a cannula inserted under the skin, linked by tubing to deliver insulin continuously. Some newer models even come tubeless for enhanced comfort and discretion.
Since the debut of the first insulin pump, the 60-kg Biostator in 1976, pumps have evolved drastically. They’re now compact enough to fit in a pocket or purse and offer advanced features for insulin delivery and blood glucose monitoring. Key improvements include programmable basal rates, which deliver insulin in varying amounts throughout the day, helping to address phenomena such as the dawn effect (early morning blood sugar spikes) without disrupting daily routines.
Insulin pumps are especially beneficial in administering rapid-acting insulin, allowing users freedom from strict meal and exercise schedules. Most pumps also feature a “bolus wizard,” which calculates the ideal insulin dose based on carb intake, current blood sugar levels, and remaining active insulin. The device’s digital history enables users to track insulin usage over time and can even be graphed for analysis on connected software.
Studies show that insulin pump users often report a higher quality of life compared to traditional insulin injection methods. Pumps make it possible to deliver very small and precise insulin doses, which is particularly valuable for young children. They can also improve HbA1c levels, relieve diabetic neuropathy pain, and even enhance sexual function, making them valuable for both type 1 and insulin-dependent type 2 diabetes patients.
The rising popularity of insulin pumps is supported by advancements in blood glucose monitoring, with newer meters requiring minimal blood, making testing less painful. Combined with growing insurance coverage, insulin pumps are becoming a preferred solution for individuals seeking better control over diabetes.